Resilience Applied to Physical Training in Tennis
06 de November, 2024
Resilience is an essential quality for any athlete, especially tennis players, who face constant physical and mental challenges in every match and training session. In the context of physical training in tennis, resilience not only refers to the ability to recover from losses or injuries but also to the skill of persisting and continuously improving despite adversity.
What is Resilience?
Resilience is the ability to adapt positively in the face of adversity, trauma, tragedy, threats, or significant stress. In tennis, this can translate into a player’s ability to recover from an injury, learn from a loss, or maintain motivation during long periods of intensive training.
The Importance of Resilience in Tennis
Resilience is crucial in tennis for several reasons:
- Injury Recovery: Tennis players are prone to injuries due to the repetitive nature of the sport. Resilience allows players not only to recover physically but also to maintain a positive mindset during rehabilitation.
- Stress Management: Tennis matches can be mentally exhausting. Resilient players can manage stress and pressure, staying calm and focused even in critical moments.
- Adaptation to Change: Playing conditions can vary (weather, court type, opponents), and resilience helps players adapt quickly to these changing circumstances.
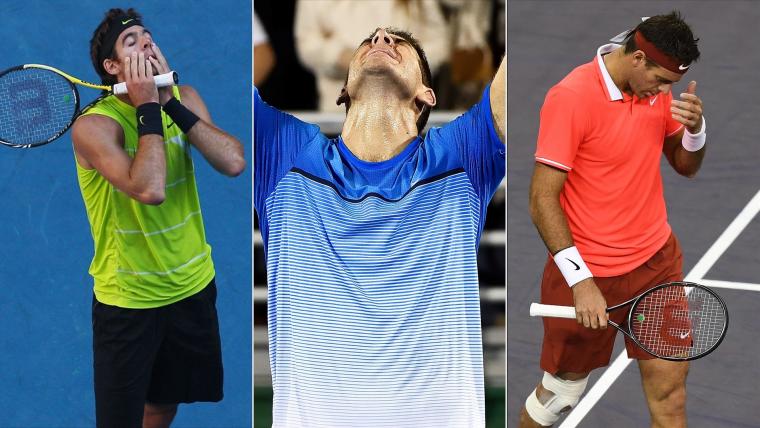

Strategies to Develop Resilience in Physical Training
Physical training not only strengthens the body but can also be a powerful tool for building resilience. Here are some strategies to incorporate resilience into tennis training:
- Strength and Conditioning Training:
-
- Gradual Progression: Gradually increasing training intensity to avoid injuries and build a solid foundation.
- Exercise Variety: Including a variety of exercises to work different muscle groups and avoid boredom and monotony.
- Active Recovery:
- Mental Training:
-
- Visualization: Practicing the visualization of game situations and how to overcome them can help prepare the mind to handle adversity.
- Relaxation Techniques: Including breathing exercises and meditation to reduce stress and improve focus.
- Goal Setting:
-
- Achievable Goals: Setting short- and long-term goals that are attainable and measurable to maintain motivation.
- Self-Assessment: Conducting regular self-assessments to adjust goals and strategies as needed.
- Social Support:
-
- Support Team: Surrounding oneself with a support team, including coaches, teammates, and family, who provide motivation and encouragement.
- Open Communication: Encouraging open and honest communication about challenges and progress.
Example of Resilience in Tennis
A notable example of resilience in tennis is Rafael Nadal. Throughout his career, Nadal has faced numerous injuries that threatened to end his career. However, his ability to recover physically, maintain a positive mindset, and return to competition at the highest level is a testament to his resilience. His focus on active recovery, proper nutrition, and mental training has been key to his continued success.
Conclusion
Developing resilience through physical training is essential for tennis players who want to achieve and maintain a high level of performance. By incorporating specific strategies into daily training, players can improve not only their strength and physical endurance but also their ability to manage stress, recover from injuries, and adapt to challenges. Resilience not only allows athletes to overcome difficulties but also prepares them for long-term success on the court and in life.
Sources:
Psychology Today: The Importance of Resilience
Resilience is essential for tennis players, helping them overcome injuries, manage stress, and stay adaptable in the face of challenges.

 ES
ES EN
EN PT
PT



